Investing can be a powerful way to grow your wealth over time, but creating a successful investment strategy can feel overwhelming, especially for beginners. One of the most effective strategies for managing risk and optimizing returns is to build a diversified investment portfolio. This guide will walk you through the steps to create a well-rounded portfolio from scratch, ensuring you’re equipped to make informed investment decisions.
Understanding Diversification: What It Means and Why It Matters
Diversification is the practice of spreading your investments across various assets to reduce risk. The idea is simple: by not putting all your eggs in one basket, you can protect your portfolio from the volatility of individual investments.
Benefits of Diversification
- Risk Reduction: A diversified portfolio is less likely to experience significant losses during market downturns because different asset classes often react differently to economic events.
- Stable Returns: By including a mix of asset types, you can smooth out the potential highs and lows of investment returns.
- Increased Opportunities: Diversification allows you to capture growth in various sectors and markets, potentially increasing your overall returns.
Resource: For a deeper understanding of diversification, explore this Investopedia article.


Step 1: Assess Your Financial Goals and Risk Tolerance
Before diving into the world of investments, it’s crucial to assess your financial goals and risk tolerance. This step will guide your investment choices and asset allocation.
Financial Goals
Identify your short-term and long-term financial goals. Are you saving for retirement, a home, or your children’s education? Understanding your objectives will help shape your portfolio.
Risk Tolerance
Your risk tolerance reflects how much risk you are willing and able to take on. Factors influencing this include:
- Age: Younger investors typically have a higher risk tolerance because they have more time to recover from potential losses.
- Income and Expenses: Your financial situation can determine how much risk you can afford to take.
- Investment Experience: More experienced investors may be comfortable taking on more risk.
Tip: Use online tools or questionnaires, such as those provided by Charles Schwab, to assess your risk tolerance.


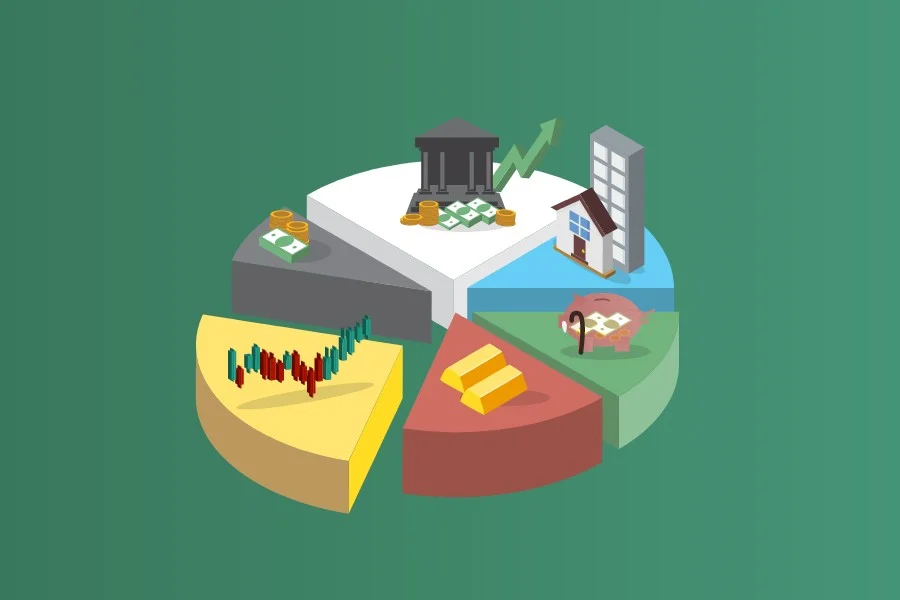
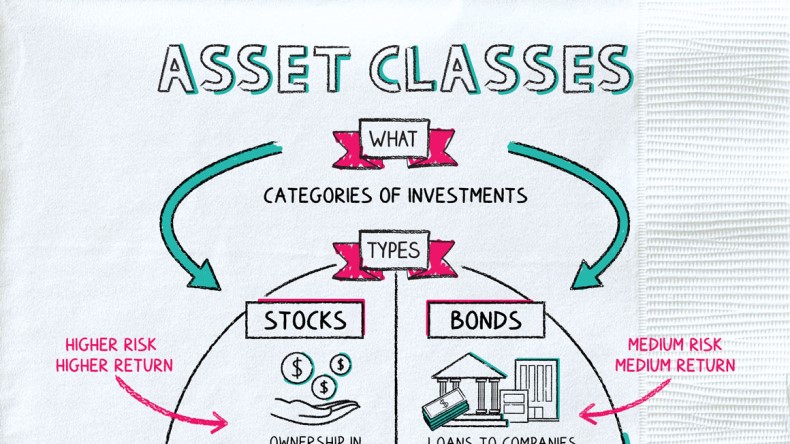
Step 2: Understand Different Asset Classes
A well-diversified portfolio typically includes a mix of various asset classes. Here’s an overview of the most common ones:
1. Stocks
Stocks represent ownership in a company and can provide high returns, especially over the long term. However, they are also more volatile than other asset classes.
- Types of Stocks:
- Growth Stocks: Companies expected to grow at an above-average rate compared to their industry.
- Value Stocks: Stocks that appear to be undervalued in price relative to their fundamental worth.
- Dividend Stocks: Companies that return a portion of their profits to shareholders as dividends.
2. Bonds
Bonds are debt securities issued by governments or corporations. They tend to be less risky than stocks and provide fixed income through interest payments.
- Types of Bonds:
- Government Bonds: Issued by national governments; considered low risk.
- Corporate Bonds: Issued by companies; generally offer higher returns than government bonds but come with higher risk.
3. Real Estate
Investing in real estate can provide rental income and long-term appreciation. You can invest directly by purchasing property or indirectly through Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs).
4. Cash and Cash Equivalents
This includes savings accounts, money market accounts, and short-term government bonds. While offering low returns, they provide liquidity and stability to your portfolio.
5. Alternative Investments
These may include commodities, cryptocurrencies, hedge funds, and private equity. Alternative investments can offer diversification benefits but often come with higher risks and less liquidity.

Step 3: Asset Allocation Strategy
Your asset allocation refers to how you divide your investments among different asset classes. The right allocation will depend on your financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment timeline.
General Guidelines for Asset Allocation
- Conservative Portfolio: More bonds and cash equivalents, fewer stocks (e.g., 20% stocks, 60% bonds, 20% cash).
- Balanced Portfolio: A mix of stocks and bonds (e.g., 60% stocks, 30% bonds, 10% cash).
- Aggressive Portfolio: More stocks for higher growth potential (e.g., 80% stocks, 20% bonds).
Resource: Consider using the Rule of 100 as a simple guideline to determine your stock and bond allocation based on your age.

Step 4: Selecting Specific Investments
Once you’ve determined your asset allocation, it’s time to choose specific investments within each asset class. Here are some tips:
Researching Investments
- Evaluate Performance: Look for historical performance data, but remember that past performance is not indicative of future results.
- Analyze Fees: High fees can erode returns over time, so compare expense ratios for mutual funds and ETFs.
- Consider Index Funds and ETFs: These can be a cost-effective way to gain diversified exposure to an entire market segment.
Tools for Research
Utilize online platforms and tools such as:
- Morningstar: For in-depth investment research and analysis.
- Yahoo Finance: For real-time stock quotes and financial news.


Step 5: Regularly Review and Rebalance Your Portfolio
Once your portfolio is set up, it’s essential to monitor it regularly and make adjustments as needed. Rebalancing involves realigning the proportions of assets in your portfolio back to your original allocation.
Why Rebalance?
- Maintain Risk Level: Over time, certain investments may grow faster than others, skewing your original asset allocation and increasing risk.
- Capture Gains: Selling overperforming assets can lock in profits and provide funds to invest in underperforming assets that may have growth potential.
How to Rebalance
- Set a Schedule: Consider rebalancing your portfolio annually or whenever an asset class deviates by a predetermined percentage from your target allocation.
- Use Automation: Many investment platforms allow you to set up automatic rebalancing, simplifying the process.


Step 6: Stay Educated and Informed
The investment landscape is constantly evolving, so staying informed is crucial for long-term success. Here are some strategies to help you keep your knowledge up to date:
1. Read Financial News and Publications
Stay updated with reputable financial news sources such as:
- The Wall Street Journal
- Bloomberg
- Financial Times
2. Follow Market Trends and Economic Indicators
Understanding economic indicators, such as interest rates and inflation, can help you make informed investment decisions. Pay attention to:
- GDP Growth
- Employment Rates
- Consumer Confidence Index
3. Consider Professional Guidance
If you feel overwhelmed or unsure, consider consulting with a financial advisor. They can provide personalized advice and help you navigate complex investment strategies.
Resource: Explore platforms like NerdWallet or SmartAsset to find financial advisors in your area.


Conclusion: Building Your Diversified Investment Portfolio
Creating a diversified investment portfolio from scratch is a systematic process that involves assessing your financial goals, understanding different asset classes, and maintaining a disciplined approach. By following these steps and avoiding common pitfalls, you can build a robust portfolio that helps you achieve your long-term financial objectives.
Remember, investing is not a one-time event but a continuous journey. Stay educated, remain flexible, and be prepared to adapt your strategy as your circumstances and the market change. With patience and persistence, you can grow your wealth and secure your financial future.
4o mini
